API Basics
This article introduces some basic concepts of APIs, in the context of using the "Send API Request" node in workflows.
What is an API?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a standardized interface that allows external users to access specific functionalities without exposing the underlying source code or implementation details. By following the API’s defined format and sending the appropriate parameters, you can retrieve data or perform operations as needed.
For example, here is a typical API that queries the location of a mobile phone number:
http://apis.juhe.cn/mobile/get?key=4c80e35a4220b955a2932a38e6511e9e&phone=15838082573
Open this URL in a browser. By modifying the number after “phone=”, you can get the location of the specified mobile number by simply pressing Enter.
This is what an API does — you only need to send the correct parameters, and the API returns the expected result. You don’t need to understand the internal logic behind it.
What Makes Up an API Request?
Calling an API means making a request to a specific URL. Each time the URL is accessed (even just refreshing the page), it counts as a request.
An API request typically includes the following components:
-
API Endpoint (URL)
The specific address where the API is made available for access.
-
Request Method
Common methods include GET, POST, and others. The method to use is determined by the API documentation.
-
Request Parameters
These are the values sent to the API to define the request.
In the earlier example, phone is a parameter in the URL.
-
Authorization/Authentication
Most APIs require verification of your identity to ensure secure access. Common authentication methods include, token, API key, and signature (sign).The API provider will give you these credentials.
-
Header
Headers contain system-level paramaters. You usually don’t need to configure headers manually unless specifically mentioned in the API documentation.
-
Body (for POST requests only)
The body holds the actual data being submitted — typically in JSON or form-data format. For example, if you want to send data from a worksheet to a third-party system, the field names and values are passed in the Body.
In Summary, to call an API successfully, you usually need to configure the following three parts:
- API URL
- Parameters
- Authentication Information
Examples
Example 1: Query Mobile Number Location (GET)
API Provider: Juhe
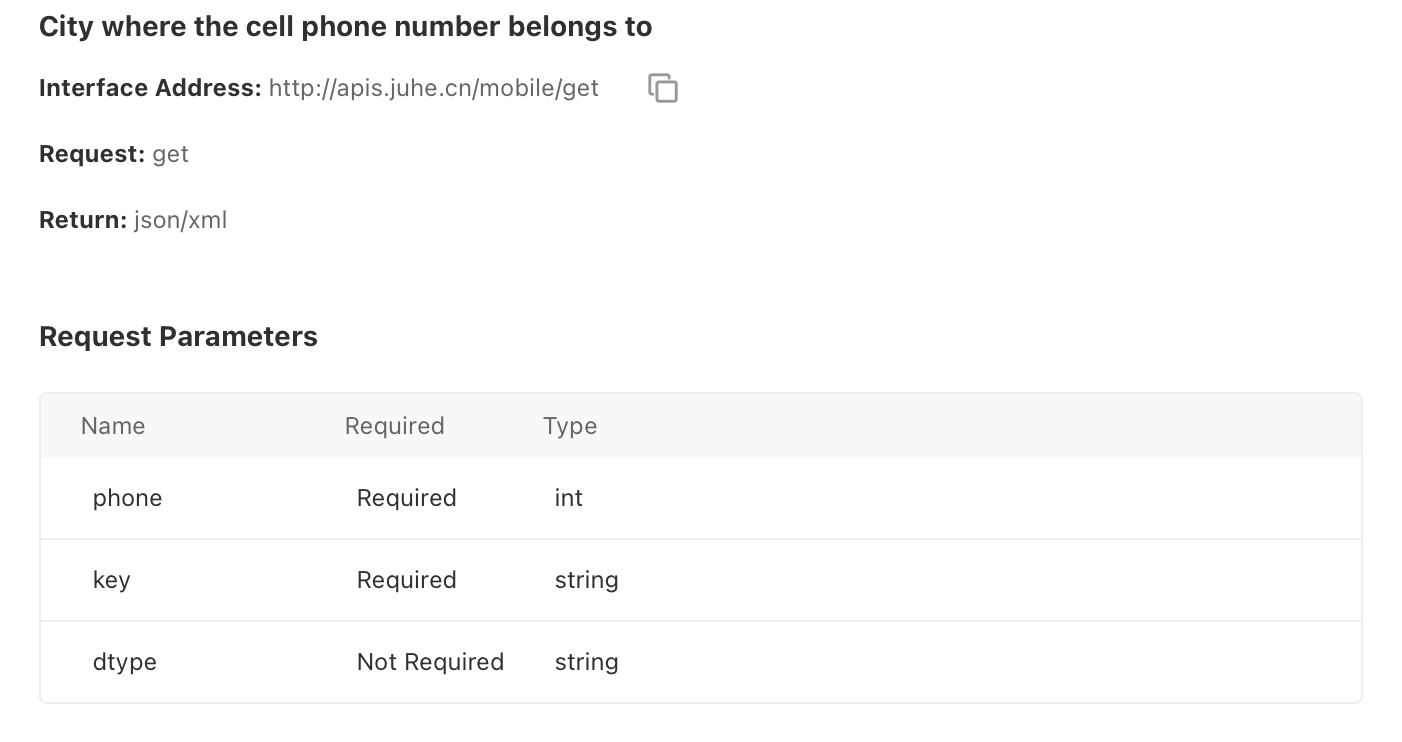
API Endpoint: http://apis.juhe.cn/mobile/get
Request Method: GET
Parameters: phone: Mobile number to be queried
key: Authentication key provided by the API vendor
Authentication: Identity is verified using the provided key, which is appended directly to the request URL. This is a simple method where the full API call is completed with a single URL.
Header: No custom headers required unless specified in the API documentation.
Body: Not applicable for GET requests.
To construct the request, concatenate the endpoint and parameters like this:
http://apis.juhe.cn/mobile/get?key=4c80e35a4220b955a2932a38e6511e9e&phone=15838082573
The API will return a response in JSON format, as shown below. You don't need to interpret this manually — the system will parse and use this data as needed.

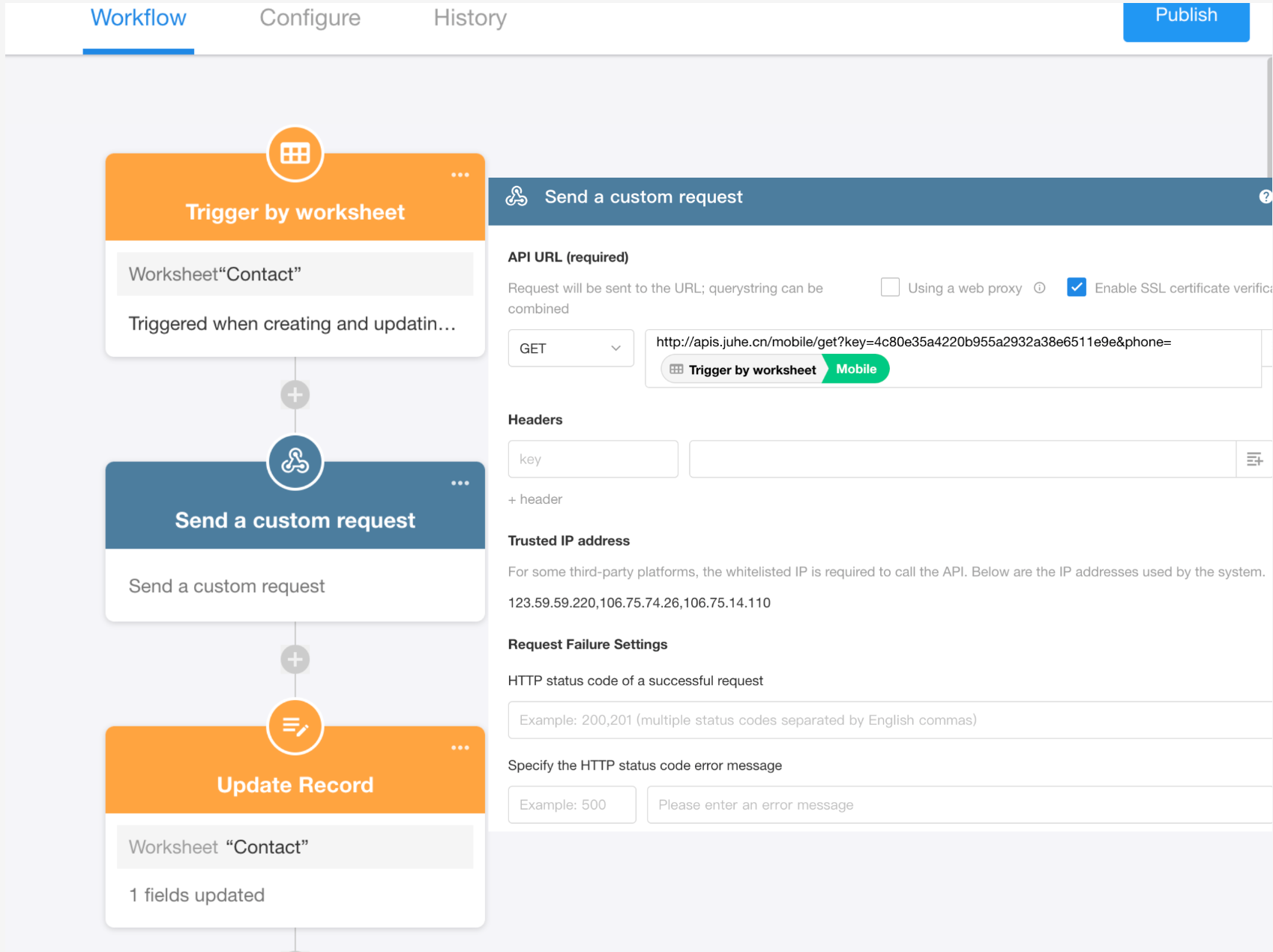
Workflow Configuration:
The API can be seamlessly integrated into a workflow using the "Send API Request" node:
-
Trigger Node: Trigger the workflow when a Contact’s mobile number is filled or updated.
-
Send API Request Node: Send a request using the phone number to retrieve its geographical attribution.
-
Update Record Node: Save the returned location info back to the Contacts record.
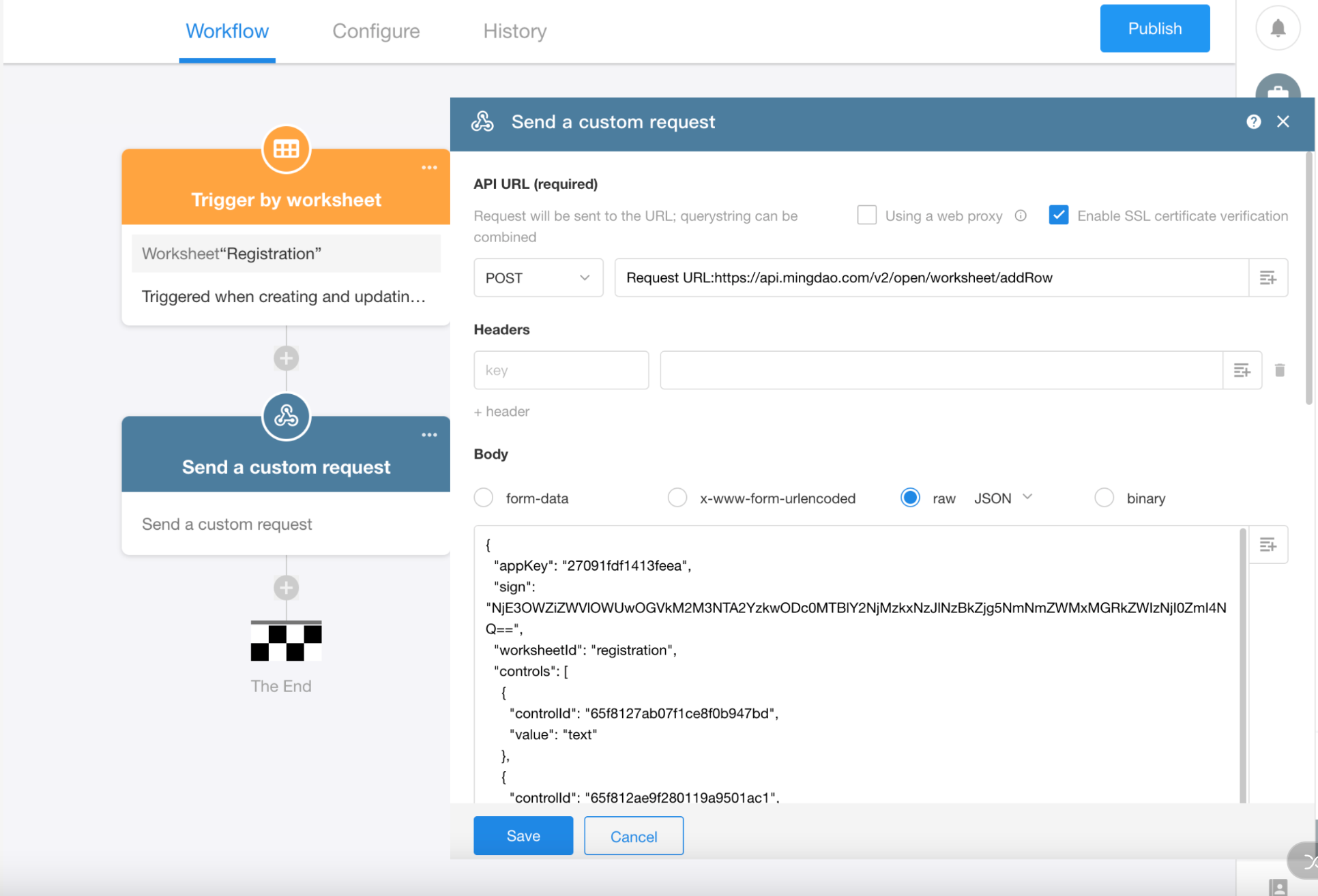
Example 2: Add a New Record to a Worksheet via API (POST Method)
In this example, we’ll demonstrate how to use a worksheet API to add a new record.
Let’s first review the API documentation:
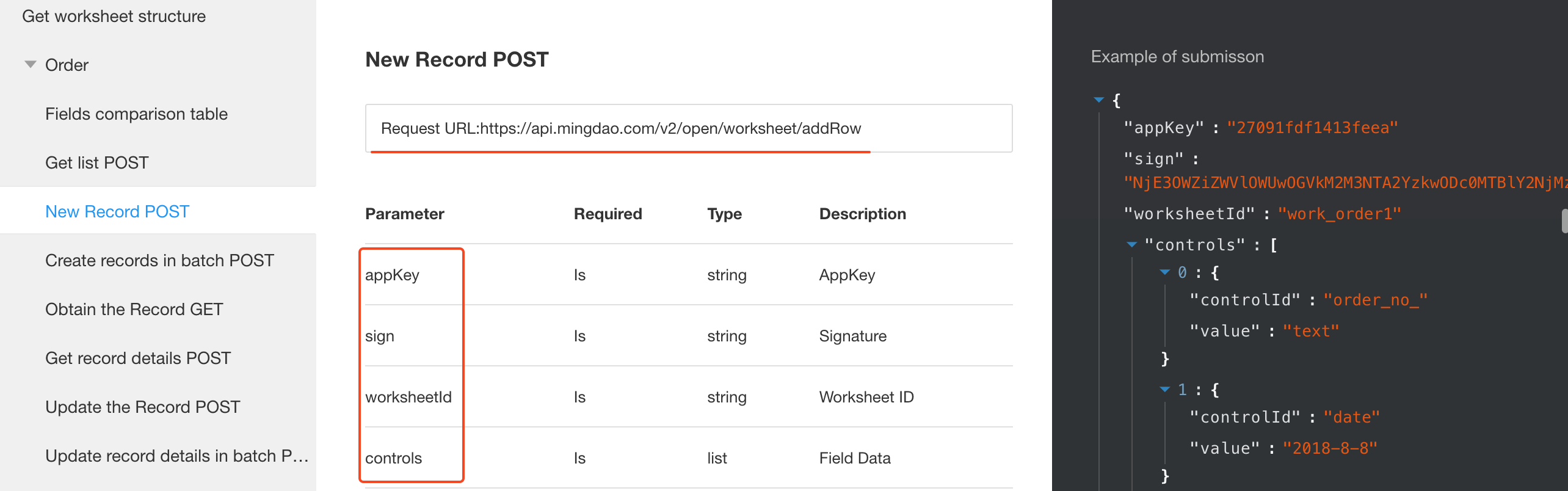
According to the documentation:
Request Method: POST
Authentication Method: appkey + sign — both should be included in the request Body.
Request Parameters: Only the URL and parameters are required for this request.
The API supports two types of Body formats:
Key-Value Pairs: This is a simple format where the left side is the parameter name and the right side is the parameter value — as shown in the image above.
Raw (application/json): In this format, the parameters are structured as a JSON object. This option typically requires developer-level configuration and JSON encoding.
Workflow Configuration:
-
Trigger Node: When a new record is added to the Registration worksheet, the workflow is triggered.
-
Send API Request Node: The workflow sends a POST request to the Personnel Registration worksheet API, adding a new record with the submitted data.