HAP Mobile Peripheral Integration User Guide
Feature Overview
The HAP Mobile App provides hardware integration capabilities such as barcode scanning and bluetooth printing, enabling rapid data entry, label printing, and ticket printing in mobile operation scenarios including warehousing, manufacturing, and retail. This guide will help you configure and use barcode scanning and bluetooth printing within the HAP Mobile App.
Supported capabilities include:
- Handheld PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants)
- PDA scan engine / camera-based barcode scanning
- Bluetooth printing with support for CPCL (Control Panel Command Language) and TSPL (TSC Print Language) command sets
1. Handheld PDAs
Handheld PDAs are commonly used industrial devices in mobile operation scenarios. They are widely applied in warehousing, manufacturing, logistics, retail inspection, and other scenarios requiring high-frequency scanning and data entry.
1.1 Supported Capabilities
Handheld PDAs support the following capabilities in the HAP Mobile App:
-
Automatic form input via barcode scan: Scan results can automatically populate text fields or barcode fields.
-
Continuous scanning: Suitable for high-volume operations such as inventory counting, receiving, and batch inspections.
-
Hardware shortcut–triggered actions: Supports executing business actions through hardware keys, such as triggering PBP (Packaged Business Process), quickly creating new records, or launching the scanning function.
-
System-level hardware integration: Enables invoking the PDA’s native scanning service, offering faster speed and higher accuracy compared with camera-based scanning.
1.2 Device Overview
Most mainstream handheld PDAs are built on the Android operating system and typically feature the following hardware characteristics:
-
Industrial-grade scan engine: Supports fast decoding of 1D and 2D barcodes.
-
Physical keys: Including scan keys, function keys (such as F1/F2), and volume keys, all of which can be custom mapped to business shortcut keys.
-
Network capabilities: Supports 4G/5G and Wi-Fi, making it suitable for mobile operation environments.
-
Robust and reliable industrial enclosure: Meets drop-resistant, dustproof, and waterproof standards (IP65–IP67).
1.3 System Limitations and Precautions
The HAP Mobile App supports two types of PDA access modes: Browser mode (H5) and the HAP App. The App is compatible with Android 5+ and supports scanning services. Additionally, the App allows hardware keys to trigger business actions.
Feature Comparison Between App and Browser Modes:
| Item | Browser Mode (H5) | App |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Scanning | Automatic input focus | Native invocation for improved performance, with configurable continuous scanning |
| Continuous Scanning | Not supported | Native support with configurable continuous scanning |
| Shortcut Keys Mapping | Not Supported | Supported |
| Back-end Operation | May be cleared by the system | May be cleared by the system |
| Access Control | The browser requires granting permissions for camera, storage, and other functions | Camera, storage, and other permissions are required |
2. PDA Dedicated Device (Infrared Scanning)
The infrared scanning module is typically integrated into industrial PDAs or dedicated scanners. It achieves high-speed recognition through a hardware laser head and is the most common hardware input method in mobile business operations.
Core capabilities include:
-
High-speed decoding: Scanning speed typically ranges from 30 to 100 ms, significantly faster than camera-based scanning.
-
Multi-symbology support: Supports one-dimensional barcodes (EAN-13, Code128, etc.) and two-dimensional codes (QR, DM, PDF417, etc.).
-
High fault-tolerance: Capable of recognizing barcodes that are creased, blurred, reflective, or otherwise difficult to read.
-
Long-distance scanning: Some devices support scanning at distances ranging from 30 cm to 150 cm.
-
System-level input method: After decoding, the scanned content is typically entered into the focused input field via the input method framework.
2.1 Browser Mode (H5 Mode)
Suitable for deployment scenarios that do not require a customized app, allowing access to the HAP H5 directly through a third-party browser on the PDA.
Working Principle: PDA scanning services typically write the scan result directly into the currently focused input field, allowing H5 forms to receive the data without additional adaptation.
Features:
- No application installation required, with a low entry barrier.
- Suitable for low-cost and rapid deployment.
2.2 Mobile App (App Mode)
Suitable for enterprises with existing custom-developed apps or a server version of HAP mobile app.
Operation Mode:
- Integration with natively developed functionalities.
- The App injects scanning events via the JSSDK.
- Hardware resources are centrally managed by the App.
- Activation Steps: On the App’s scanning page, tap the settings icon in the upper-right corner and enable “Enable Dedicated Scanning Device”.
Advantages:
- Enables deep access to system-level APIs.
- Provides more stable scanning performance.
- Continuous scanning.
3. PDA Shortcut Keys Configuration
PDAs are typically equipped with left and right physical scan keys, function keys (F1/F2), and top buttons. Through key mapping, hardware keys can trigger specific actions within HAP, enabling a highly efficient 'key-to-action' experience.
3.1 Shortcut Key Trigger Logic
PDA hardware keys typically have two trigger modes: Key-initiated app launch; key-triggered broadcast.
-
Key-initiated app launch: The PDA supports configuring hardware keys to launch the application with parameters, which are then received by the app to execute the corresponding subsequent actions.
-
Key-triggered broadcast: Industrial PDAs support key-triggered broadcasts (Broadcast Intent), which are received by the application to execute subsequent actions.
3.2 Key mapping method (using iData as an example)
The PDA provides a Key Mapping Tool that enables mapping a hardware key to a designated action and its corresponding parameters.
Steps for key mapping (using iData as an example):
-
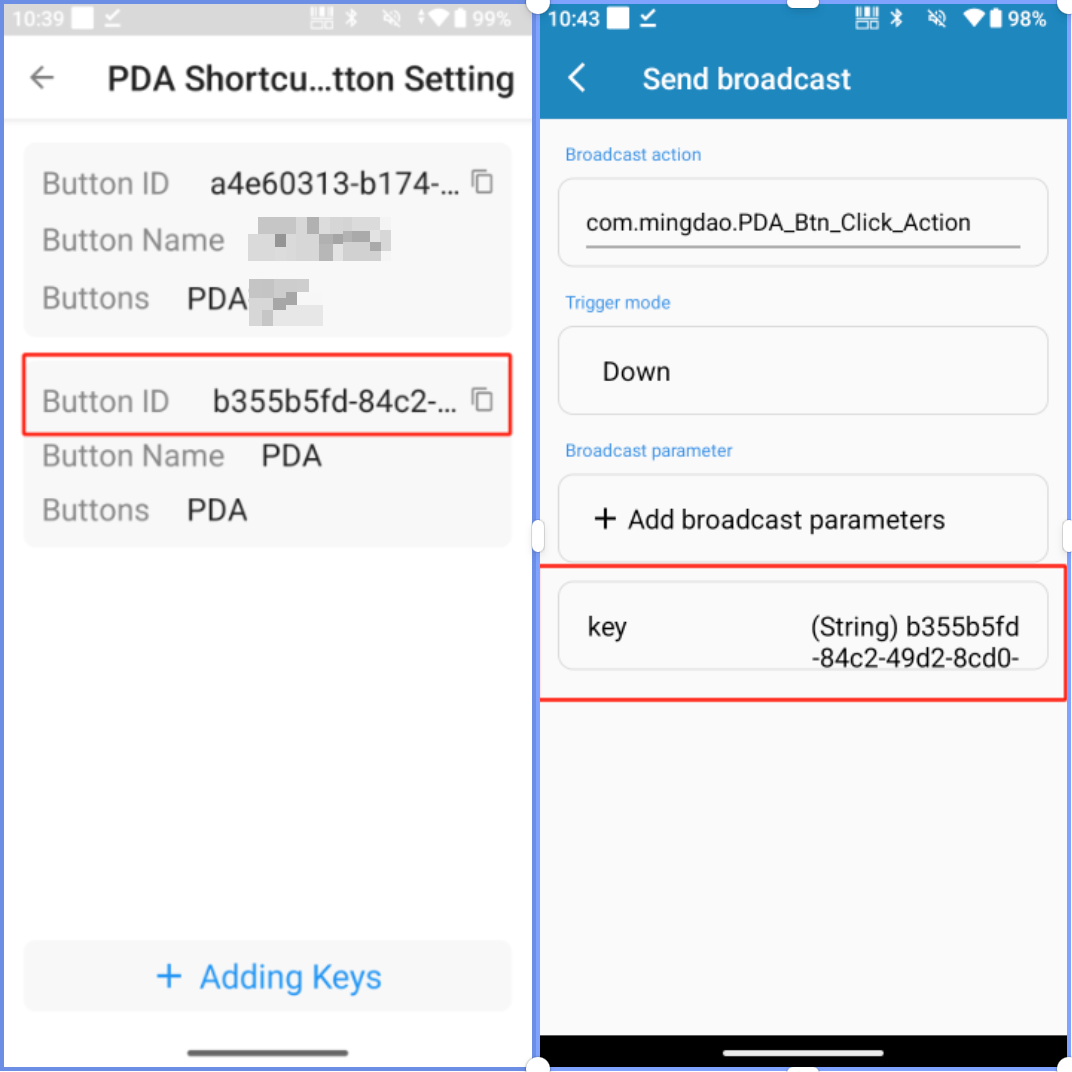
Within the app, identify the button to be triggered and copy its associated button ID.
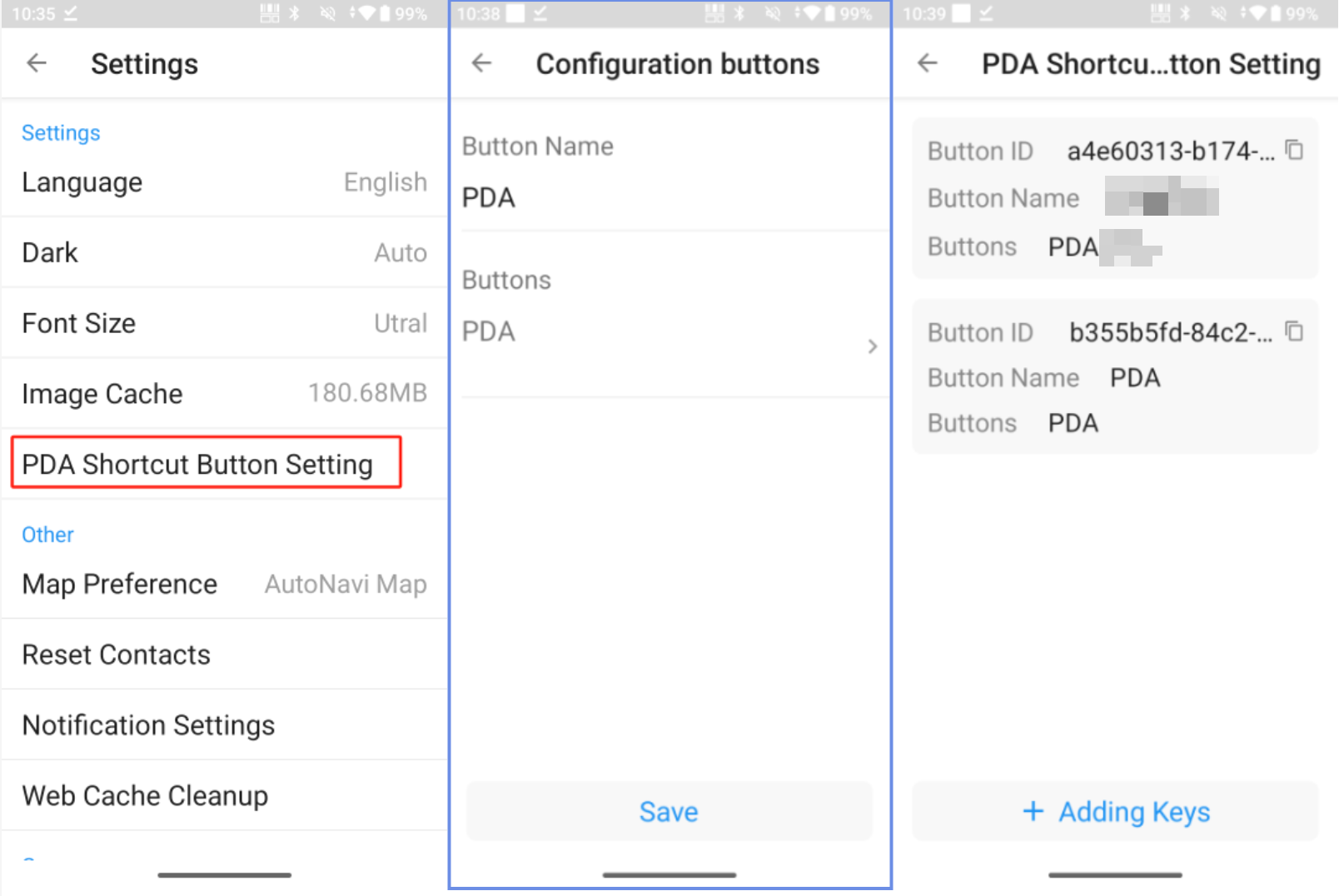
-
Create a new shortcut button on the PDA and bind it to the corresponding button in HAP.
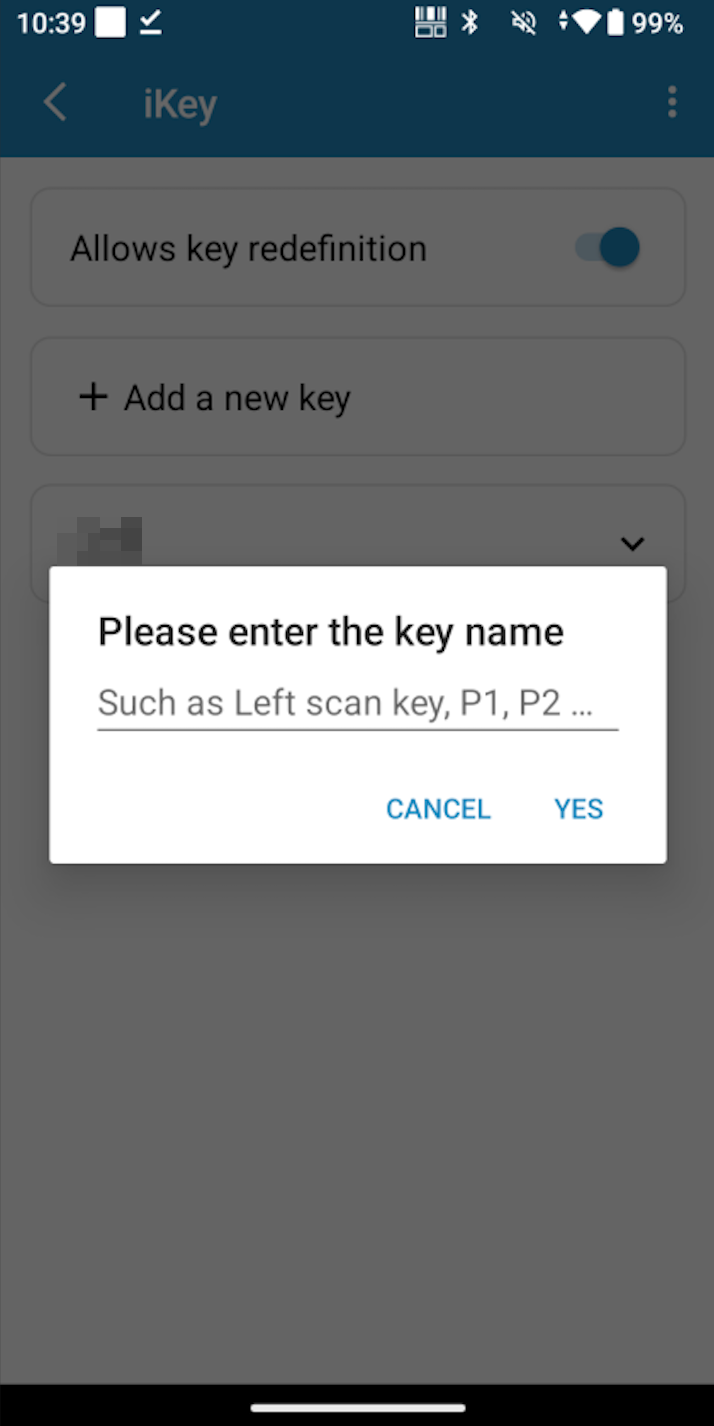
-
Option 1 (compatible with lower Android versions):
In the key settings, configure the key to send broadcasts, and set the broadcast action to com.mingdao.PDA_Btn_Click_Action
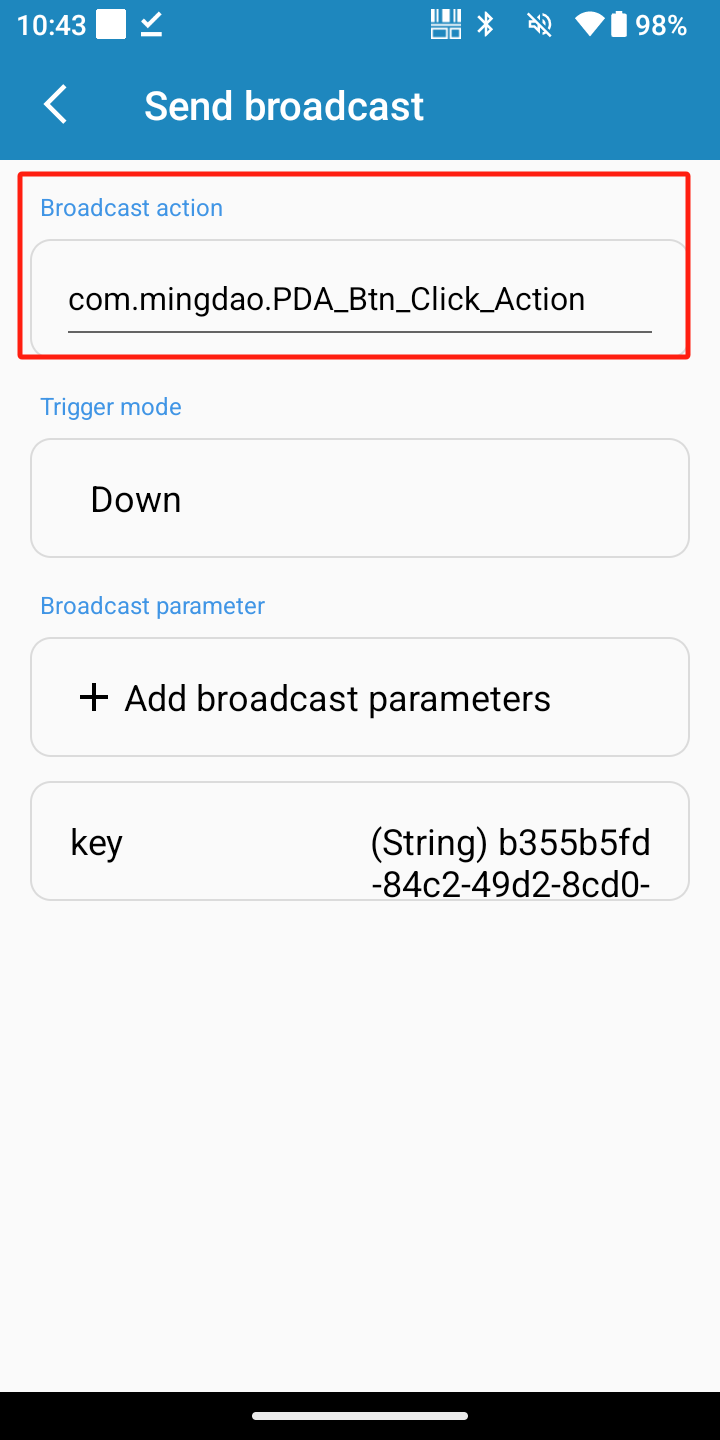
Add broadcast parameters: set the key to 'key' and the value to the button ID copied from the app.
-
Option 2 (intended to address higher Android versions where apps are prohibited from starting activities in the background)
Issue: In higher Android versions, applications cannot be launched from the background when triggered by broadcasts.
Solution – configure the key to launch the application directly.
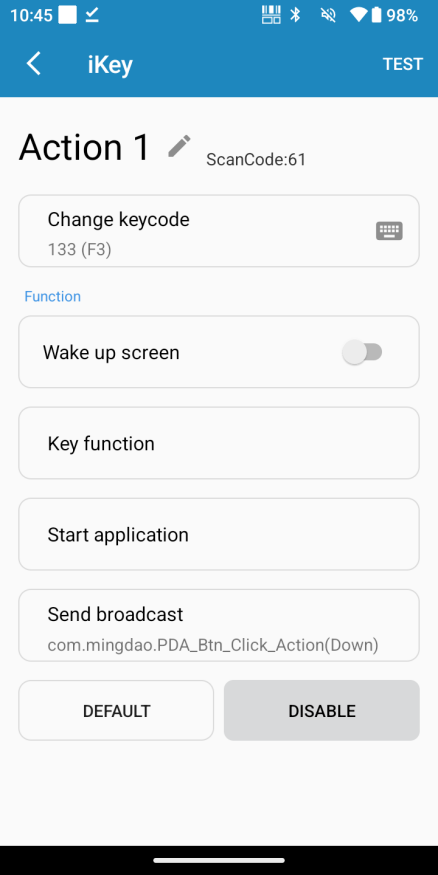
Add application launch parameters: set the key to 'key' and the value to the button ID.
-
Before using, the app must be turned on to register for broadcasts. Once turned on, the app can be moved to the back end.
3.3 Precautions
- Supports mapping hardware keys to buttons within the app.
- Supports triggering via broadcast (note: higher Android versions may not support launching via broadcast; in such cases, use the 'Launch App' method).
- The action must be set to com.mingdao.PDA_Btn_Click_Action
- Set the parameter key to the ID of the button in HAP.
- The app must be turned on first to complete broadcast registration.
- After registration, the app can run in the background and operate normally.
4. Bluetooth Printer
Bluetooth printing is only supported in the HAP Mobile App. The app establishes an SPP (Serial Port Profile) connection with the printer through the device’s built-in Bluetooth module. H5 pages do not have native Bluetooth communication capabilities; all printing operations are executed via the App through JSBridge.
4.1 Supported Types
The current app supports two mainstream command sets — CPCL and TSPL — covering most portable label printers.
4.2 Bluetooth Printing Invocation Flow in the App (CPCL / TSPL)
-
Configure Template
Configure printing templates in HAP according to business requirements. Currently, Bluetooth printing only supports HAP barcode and QR code templates. A template typically includes:
- Label Size
- Text Layout
- Barcode / QR Code
- Variable Placeholders (e.g., Product Name, Batch Number, Storage Location)
-
Select Template in the App
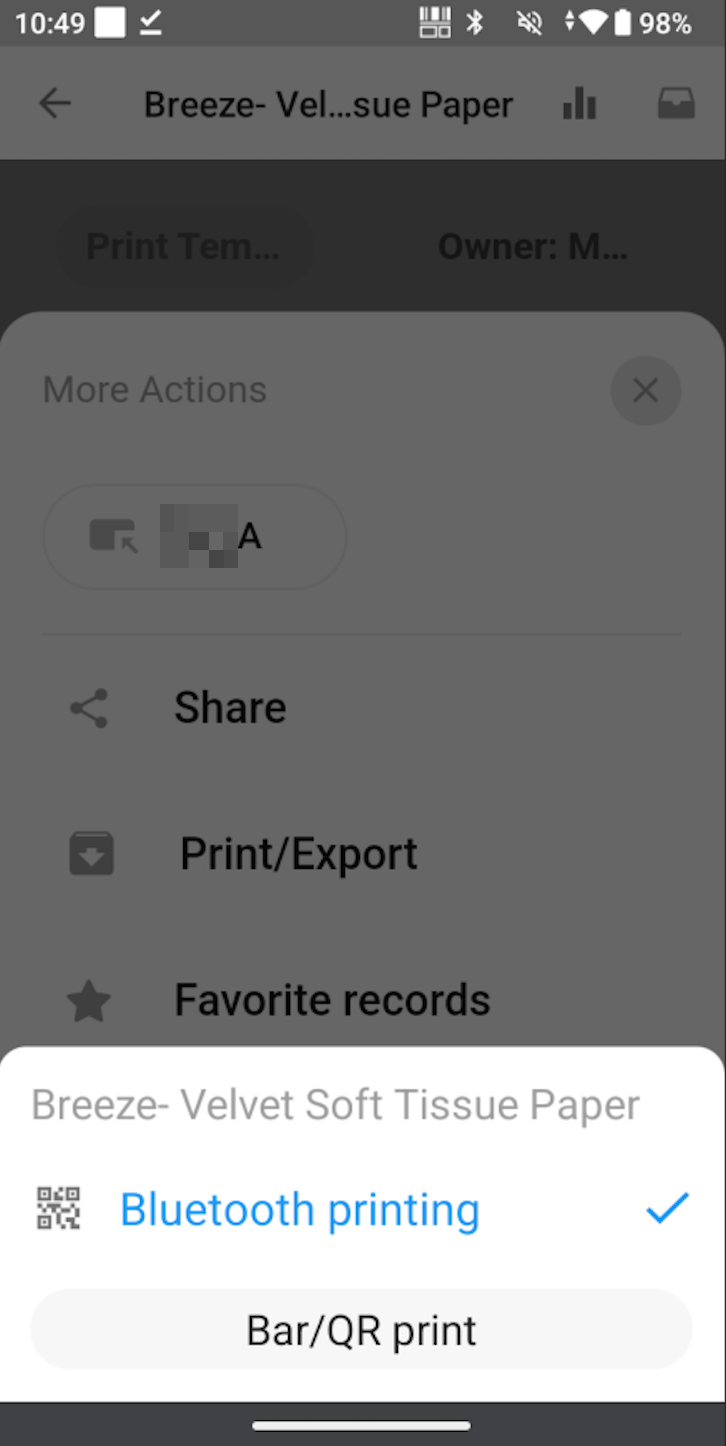
-
Select and search for Bluetooth Printers
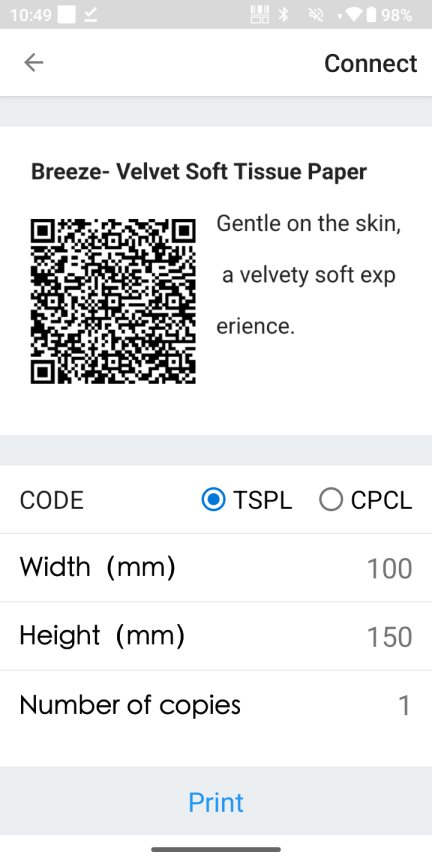
-
Click 'Print' to send the file to the physical printer for output