Workflow Parameters
I. What are workflow parameters
Workflow parameters can be considered as special objects defined within a workflow, similar to fields in a worksheet. Users can store information in these parameter objects, such as:
-
Specific field values
-
Calculation results from calculation nodes
-
Data passed from other workflows
This information can be flexibly referenced and used within the workflow. Workflow parameters act as versatile "information hubs", playing a key role in storing and transferring data during workflow execution.
Note: Parameter values are cleared and reset after workflow completion.
II. Defining workflow parameters
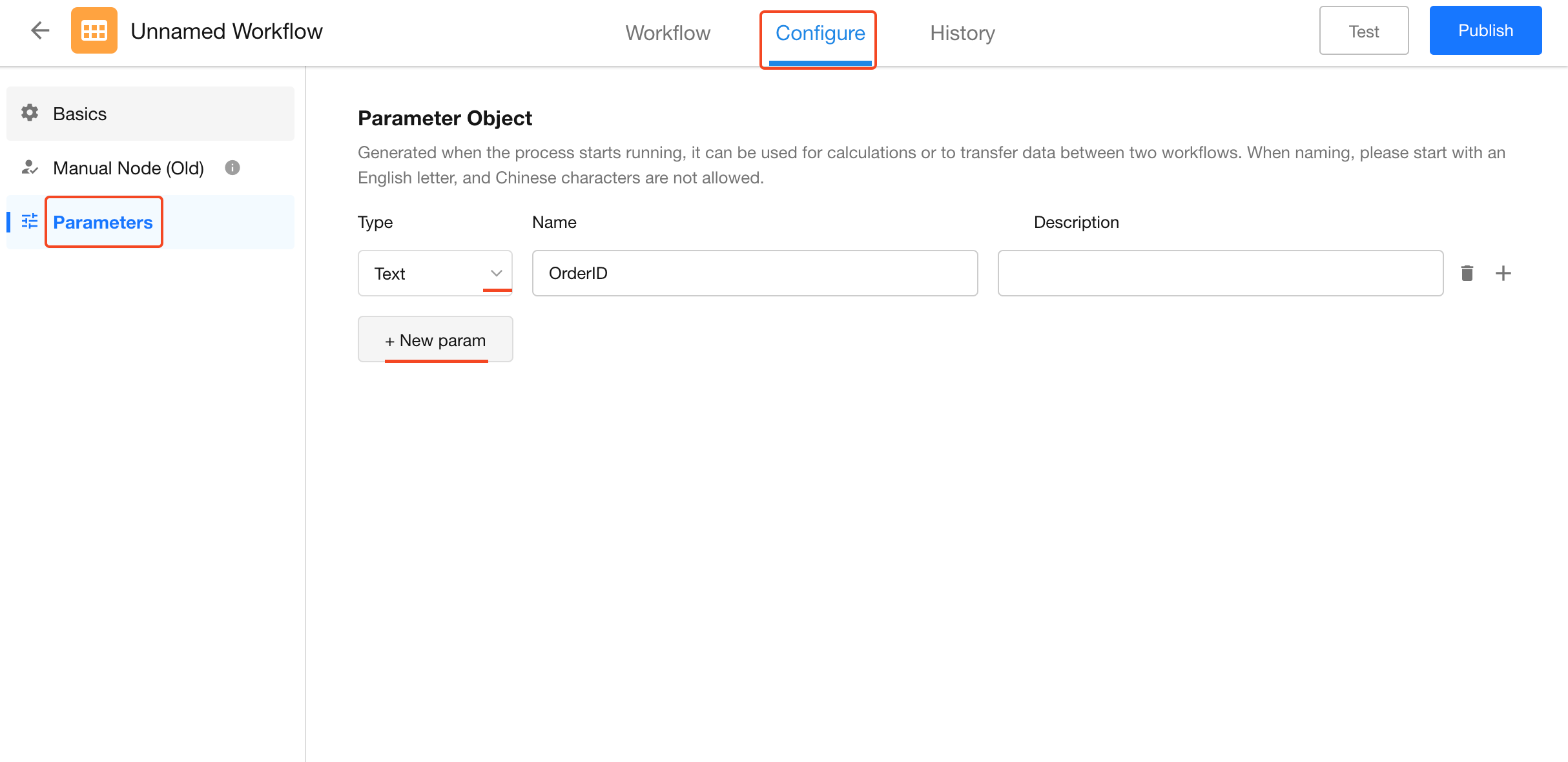
Create required parameters in the workflow's global configuration - there are no limits on the number of parameters.
-
Parameter Types
Currently supports: Text, Number (currency), Date/Time, Regular arrays, Object arrays, Personnel, Departments,Organizational roles
Parameter types must be correctly configured for proper value assignment.
-
Parameter Naming
Must begin with a letter.
Can include numbers and underscores.
-
Parameter Description
Provides explanatory text that displays during parameter configuration.
III. Assigning values to parameters
Parameters have no initial values when created. Value assignment occurs during workflow execution through two methods:
-
Using the "Update Parameters" node to assign values
-
Passing values via the "Subprocess" node to complete assignment
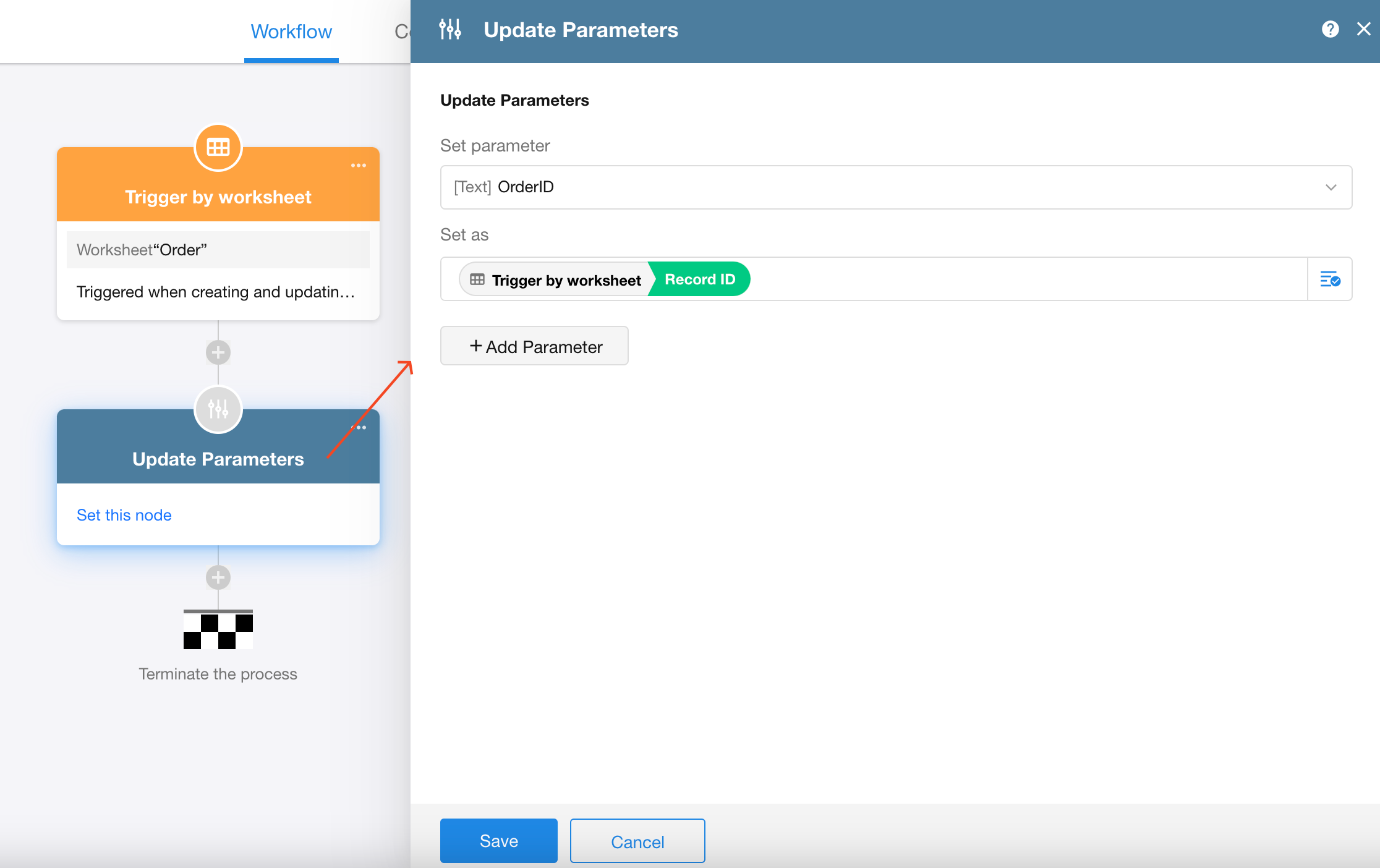
1. Update parameters of the workflow
Use the “Update Parameters” node to directly assign values to parameters within the current workflow. Similar to the “Update Record” node, parameters can be treated like fields and updated accordingly.
2. Assign values to parameters in a subprocess
Assign values to subprocess parameters within the “Subprocess” node:
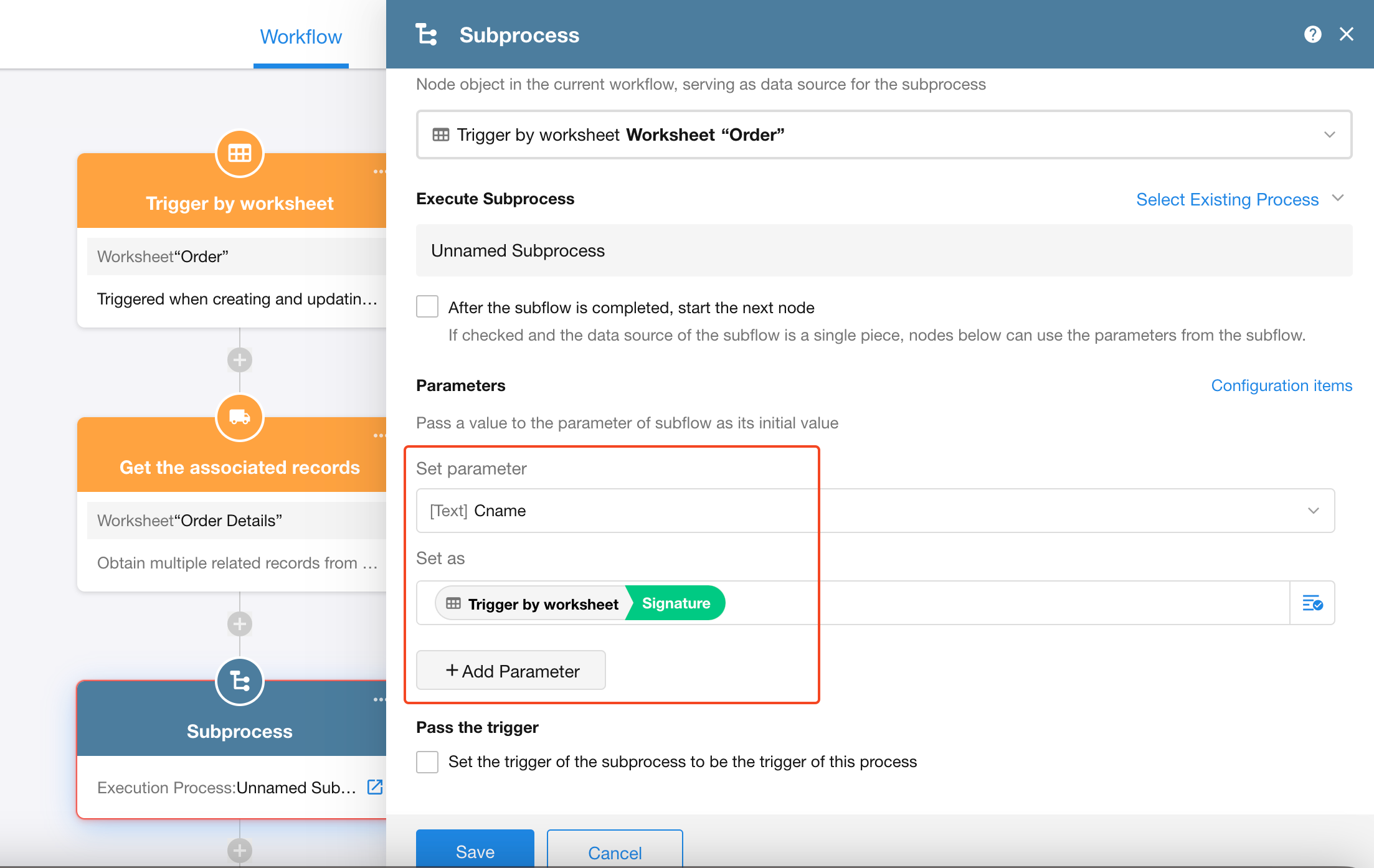
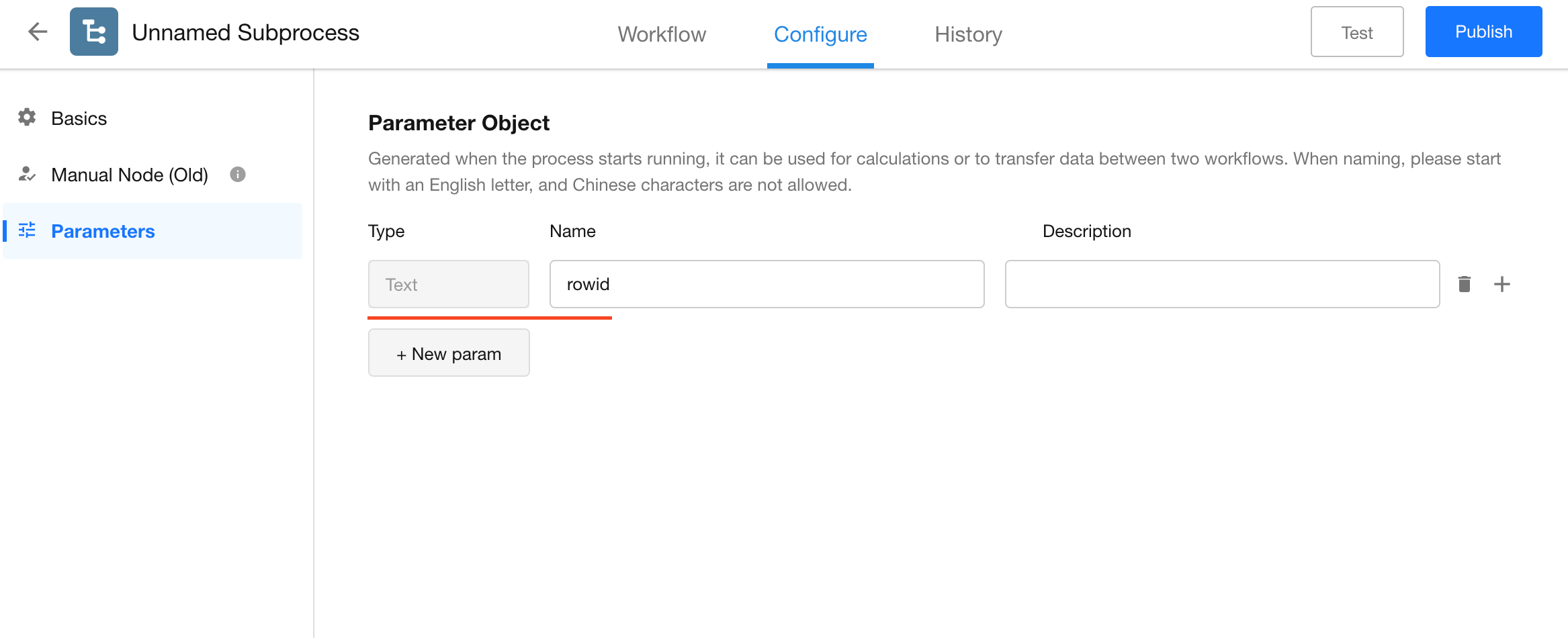
If parameters have not yet been configured in the subprocess, there are two ways to add them:
-
Click “Configuration items” on the right side of the “Subprocess” node to quickly add parameters to the subprocess.
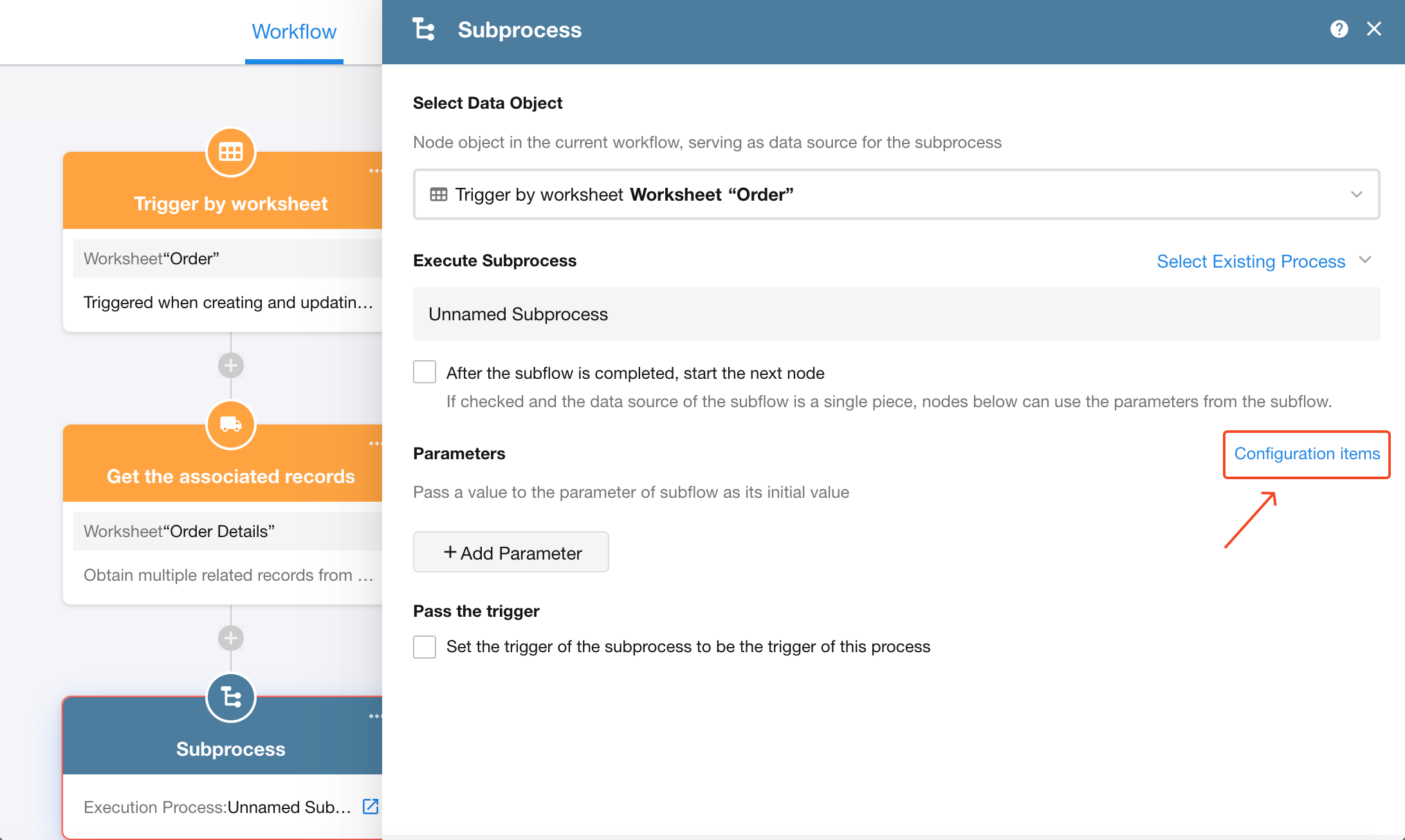
-
Navigate to the subprocess configuration page and add parameters using the standard method.
IV. Example
Typical workflow models that require the use of parameters:
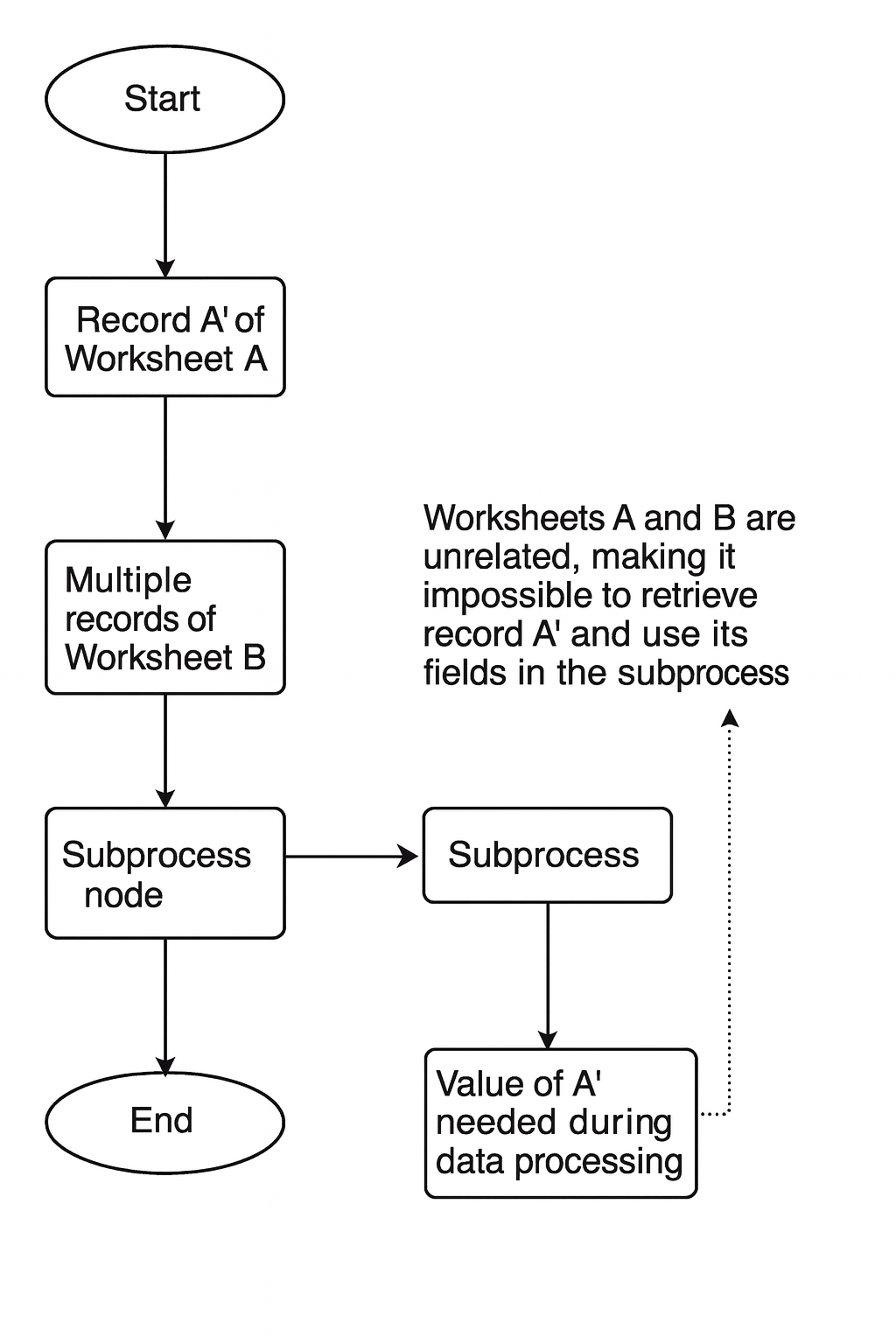
As shown above, Worksheet A and Worksheet B are not linked. In a subprocess, it's not possible to directly access the values from record A' because they belong to different workflows and cannot be referenced. However, by passing parameters, the subprocess can locate record A' based on the parameter value, enabling access to the data from record A'.
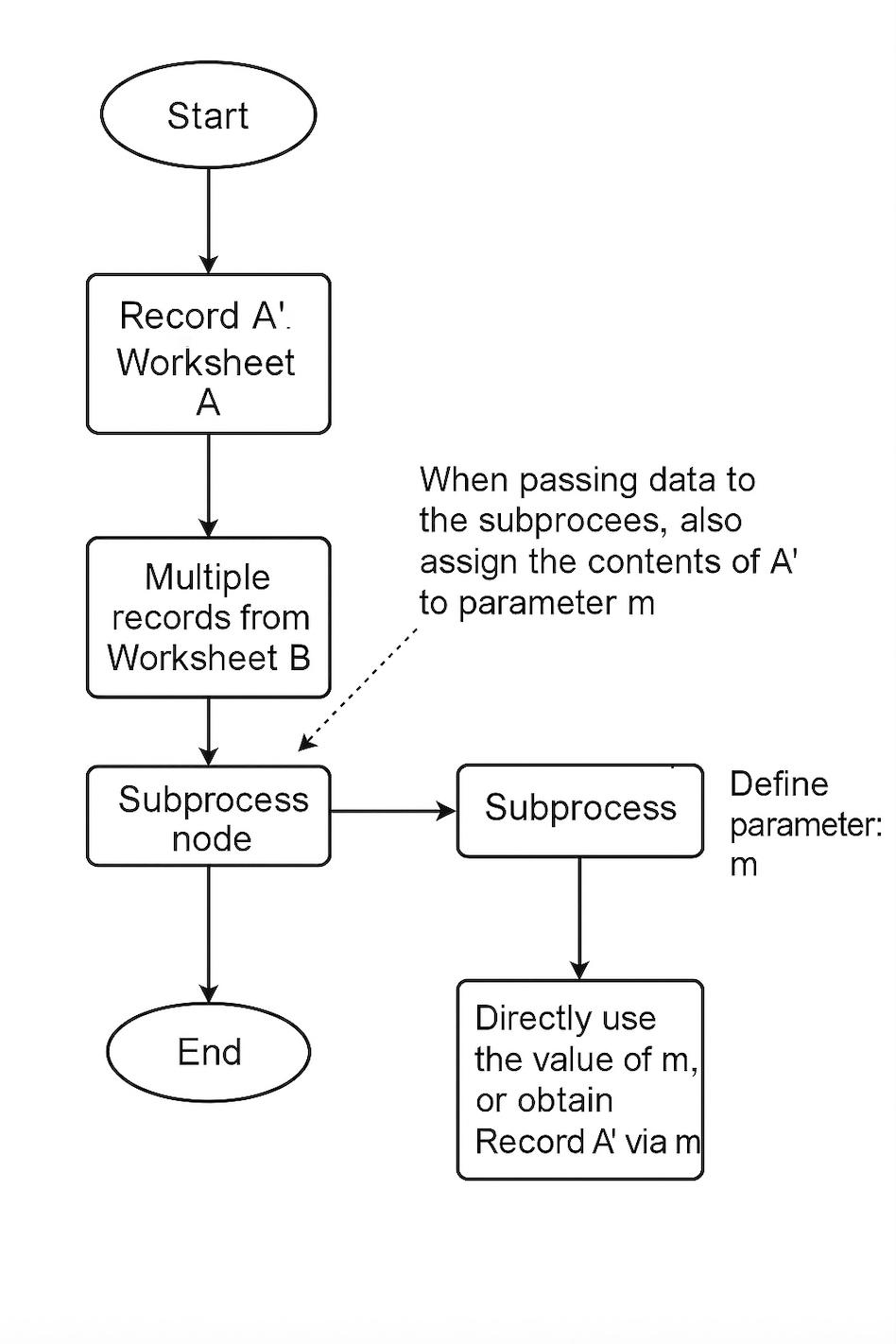
Use Case
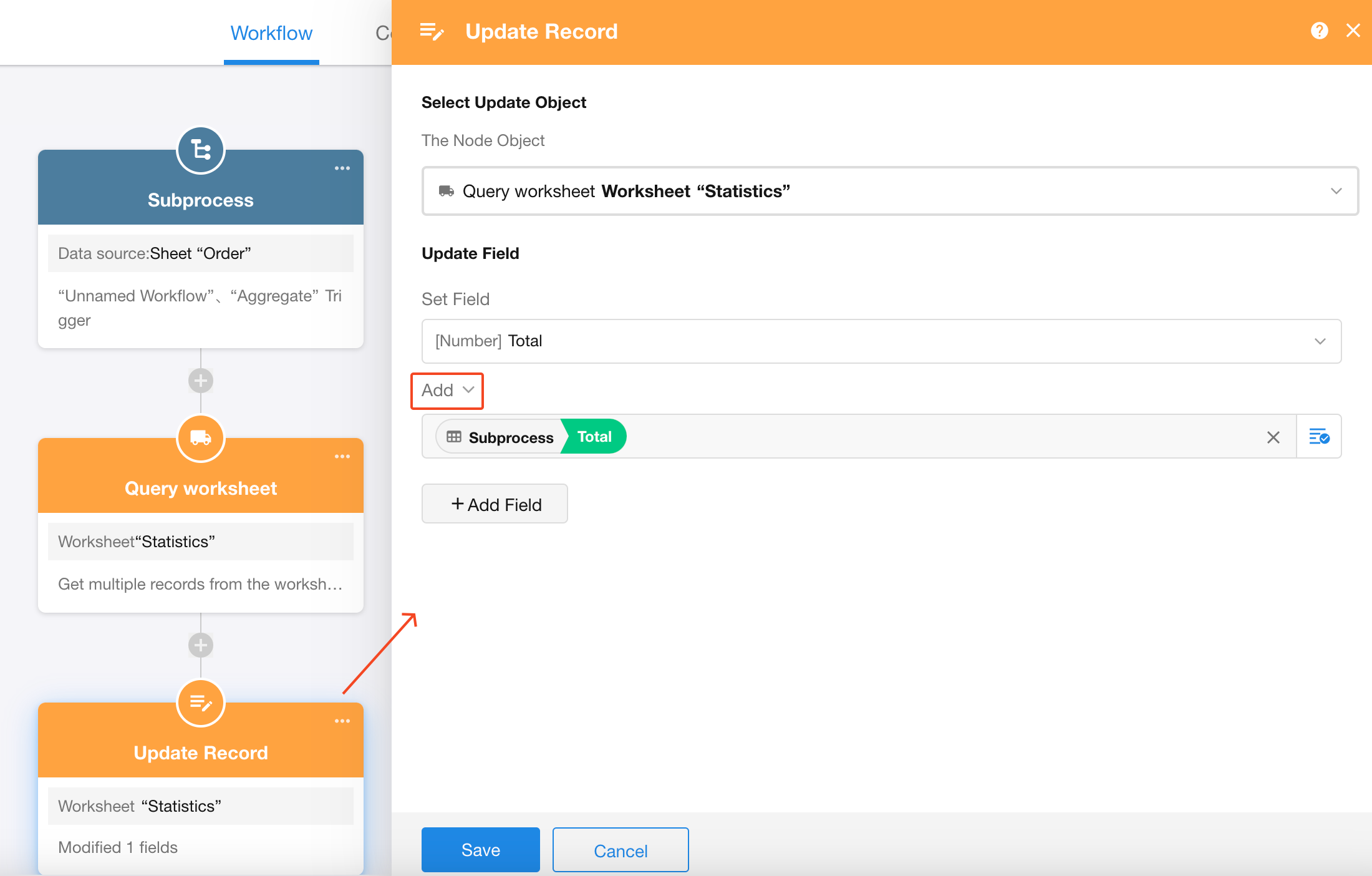
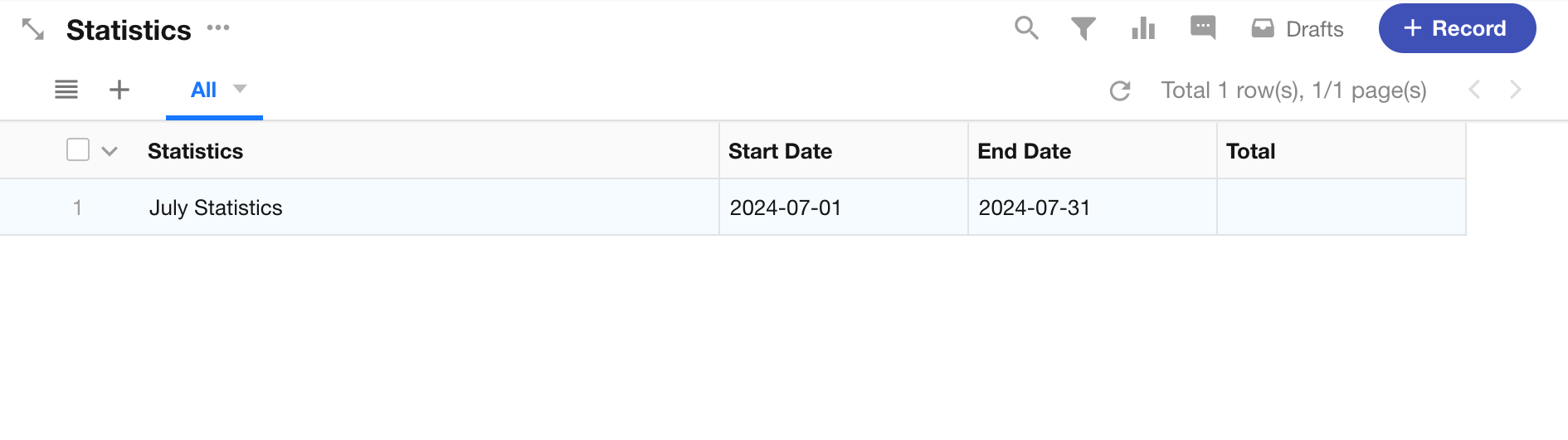
In a Statistics worksheet, a statistics record is created containing a Start Date, End Date, and a Total field. The workflow needs to, based on this statistical record, find all order records that meet the specified criteria, aggregate them, and update the total into the statistical record.
Worksheet Configuration
1. Statistics Worksheet
2. Order Worksheet
In a statistics record, after entering the start date and end date, the workflow will automatically calculate the total amount of valid orders within that time period and write the result into the “Total” field.
Workflow Configuration
Main workflow
We create a custom button-triggered workflow. Once the workflow is triggered, it retrieves records from the Order worksheet based on certain conditions and passes the data to the subprocess for execution.
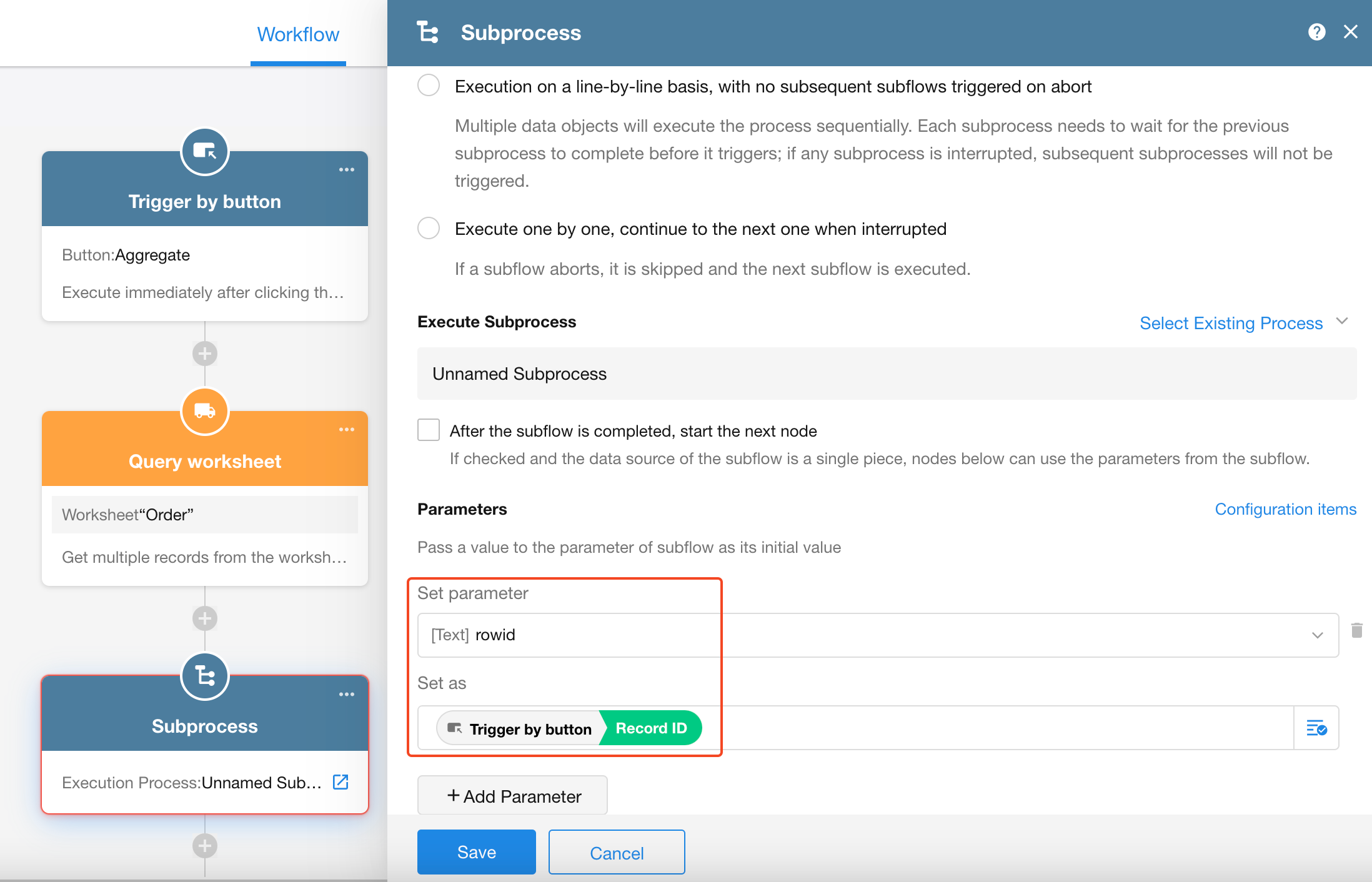
Before configuring the parameters, make sure to define the parameters in the subprocess first.
Subprocess
When the subprocess starts, the parameters will already have initial values. Then, using the “Get Single Data” node, the corresponding statistical record is located.
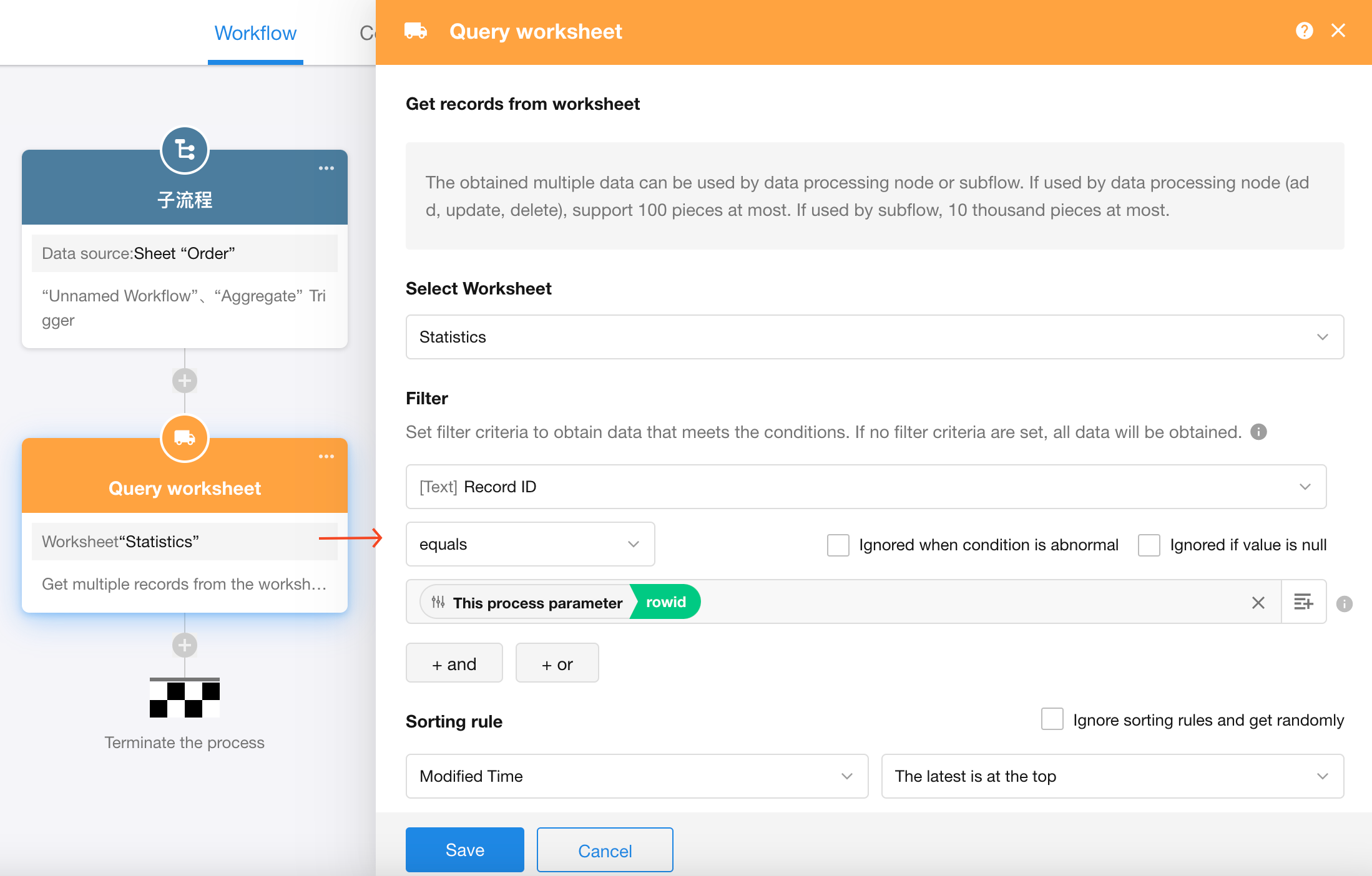
Finally, the order amount is added to the “Total” field in the statistics record.